alleen voor onderzoeksdoeleinden
R788 (Fostamatinib) Disodium Syk remmer
Cat.nr.S2206
Chemische structuur
Molecuulgewicht: 624.42
Kwaliteitscontrole
| Gerelateerde doelwitten | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Overig Syk Inhibitoren | R406 R406 (free base) PRT062607 (P505-15) HCl Entospletinib (GS-9973) Piceatannol BAY 61-3606 dihydrochloride PRT-060318 2HCl TAK-659 Hydrochloride Lanraplenib (GS-SYK) RO9021 |
Celkweek, behandeling & werkzame concentratie
| Cellijnen | Assaytype | Concentratie | Incubatietijd | Formulering | Activiteitsbeschrijving | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramos | Function assay | Inhibition of SYK in human Ramos cells, IC50 = 0.267 μM. | 23350847 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klik om meer experimentele gegevens over cellijnen te bekijken | ||||||
Chemische informatie, opslag en stabiliteit
| Molecuulgewicht | 624.42 | Formule | C23H24FN6O9P.2Na |
Opslag (vanaf de datum van ontvangst) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-nr. | 1025687-58-4 | SDF downloaden | Opslag van stamoplossingen |
|
|
| Synoniemen | Tamatinib Fosdium | Smiles | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
Oplosbaarheid
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 12 mg/mL
(19.21 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molariteitscalculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo formulatiecalculator (heldere oplossing)
Stap 1: Voer onderstaande informatie in (Aanbevolen: een extra dier om rekening te houden met verlies tijdens het experiment)
Stap 2: Voer de in vivo formulering in (Dit is alleen de calculator, geen formulering. Neem eerst contact met ons op als er geen in vivo formulering is in de sectie oplosbaarheid.)
Berekeningsresultaten:
Werkconcentratie: mg/ml;
Methode voor het bereiden van DMSO-moedervloeistof: mg geneesmiddel vooropgelost in μL DMSO ( Concentratie moedervloeistof mg/mL, Neem eerst contact met ons op als de concentratie de DMSO-oplosbaarheid van de batch van het geneesmiddel overschrijdt. )
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO moedervloeistof, voeg daarna toeμL PEG300, mengen en verhelderen, daarna toevoegenμL Tween 80, mengen en verhelderen, daarna toevoegen μL ddH2O, mengen en verhelderen.
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO moedervloeistof, voeg daarna toe μL Maïsolie, mengen en verhelderen.
Opmerking: 1. Zorg ervoor dat de vloeistof helder is voordat u het volgende oplosmiddel toevoegt.
2. Zorg ervoor dat u het/de oplosmiddel(en) in de juiste volgorde toevoegt. U moet ervoor zorgen dat de verkregen oplossing, bij de vorige toevoeging, een heldere oplossing is voordat u verdergaat met het toevoegen van het volgende oplosmiddel. Fysieke methoden zoals vortexen, ultrasoon of een warmwaterbad kunnen worden gebruikt om het oplossen te bevorderen.
Werkingsmechanisme
| Kenmerken |
Clinically used oral formulation of R406.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Syk
(Cell-free assay) 41 nM
|
| In vitro |
R935788 is een methyleenfosfaat-prodrug van R406, die in vivo snel kan worden omgezet in R406. R406 (in vitro actieve vorm van R935788) remt selectief Syk-afhankelijke signalering met EC50-waarden variërend van 33 nM tot 171 nM, krachtiger dan Syk-onafhankelijke routes in verschillende cellen. R406 remt de cellulaire proliferatie van een verscheidenheid aan diffuse grote B-cellymfoom (DLBCL) cellijnen met EC50-waarden variërend van 0,8 μM tot 8,1 μM. R406-behandeling vermindert de basale fosforylering van BLNK, Akt, glycogeensynthasekinase-3 (GSK-3), forkhead box O (FOXO) en ERK niet alleen in cellen met hoge (TCL-002) maar ook in cellen met lage niveaus van gefosforyleerd Syk (TCL1-551). Bovendien remt R406 het anti-IgM-geïnduceerde Bcr-signaal in TCL1-leukemieën volledig. Ondanks de hogere niveaus van constitutief actief Syk in TCL1-leukemieën is R406 niet selectief cytotoxisch voor de leukemische cellen.
|
| Kinase Assay |
In vitro fluorescentiepolarisatie-kinase-assays
|
|
R406 (in vitro actieve vorm van R935788) wordt serieel verdund in DMSO en vervolgens verdund tot 1% DMSO in kinasebuffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7,4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,1 mg/mL geacetyleerd BGG). ATP en substraat in kinasebuffer worden bij kamertemperatuur toegevoegd, wat resulteert in een uiteindelijke DMSO-concentratie van 0,2%. De kinasereacties worden uitgevoerd in een eindvolume van 20 μL met 5 μM HS1-peptide substraat en 4 μM ATP en gestart door toevoeging van 0,125 ng Syk in kinasebuffer. De reactie mag 40 minuten bij kamertemperatuur verlopen. De reactie wordt gestopt door de toevoeging van 20 μL PTK-quenchmix met EDTA/anti-fosfotyrosine-antilichaam (1× finaal)/fluorescerende fosfopeptide-tracer (0,5× finaal) verdund in FP-verdunningsbuffer. De plaat wordt 30 minuten in het donker bij kamertemperatuur geïncubeerd en vervolgens afgelezen op een Polarion fluorescentiepolarisatieplaatlezer. Gegevens worden omgezet om de hoeveelheid aanwezig fosfopeptide te bepalen met behulp van een kalibratiecurve die is gegenereerd door competitie met de fosfopeptide-competitor die in de Tyrosine Kinase Assay Kit wordt geleverd. Voor IC50-bepaling wordt R406 getest in elf concentraties in duplo en curve-fitting wordt uitgevoerd door niet-lineaire regressieanalyse met behulp van Prism GraphPad Software.
|
|
| In vivo |
Aangezien de plasmahalfwaardetijd van R406 bij muizen minder dan 2 uur bedraagt, wordt R935788 in 3 verdeelde doses met intervallen van 3 uur toegediend om een continue Syk-remming te bieden gedurende elke behandelingsdag, ter nabootsing van de langere plasmahalfwaardetijd bij mensen (15 uur). Ondanks het relatief bescheiden cytotoxische effect in vitro, remt R935788 de proliferatie en overleving van leukemische cellen in vivo aanzienlijk, wat verband houdt met het blokkeren van antigeen-afhankelijke B-celreceptor (Bcr)-signalering in plaats van remming van constitutieve Syk-activiteit. R935788-behandeling met 80 mg/kg/dag gedurende 18-21 dagen remt de tumorgroei van TCL1-002, TCL1-551 en TCL1-870 bij muizen potent met ondetecteerbare leukemische CD5+/B220+-cellen op de laatste behandelingsdag, verlengt de overleving van de behandelde muizen significant met een mediane overleving die is toegenomen van 45/46 dagen naar 170/172 dagen, en roeit de maligne cellen bij een aanzienlijk deel van de muizen na een follow-upperiode van 6 maanden volledig uit zonder de productie van normale B-lymfocyten te beïnvloeden. R935788-behandeling induceert ook een vroege en voorbijgaande migratie van zowel normale als maligne B-cellen van milt en lymfeklieren naar perifeer bloed, wat vervolgens wordt gevolgd door selectieve groei-inhibitie van de maligne B-celpopulatie. Bovendien is R935788 ook effectief tegen spontaan ontwikkelende TCL1-leukemieën in Eμ-TCL1-transgene muizen.
|
Referenties |
|
Toepassingen
| Methoden | Biomarkers | Afbeeldingen | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-JAK2 / JAK2 / p-SRC / SRC / p-FAK / FAK / p-SYK / SYK / p-ERK / ERK p-SYK(525-526) / t-SYK / p-SYK(323) / p-BTK / t-BTK p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-AKT / AKT |

|
29340070 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
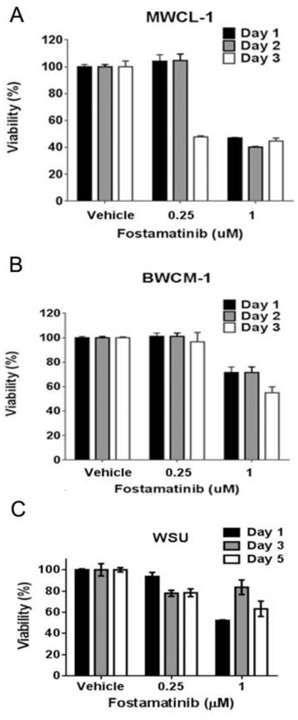
|
25748087 |
Informatie over klinische proeven
(gegevens van https://clinicaltrials.gov, bijgewerkt op 2024-05-22)
| NCT-nummer | Werving | Aandoeningen | Sponsor/medewerkers | Startdatum | Fasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Sickle Cell Disease|Hb-SS Disease|Hemoglobin S|Disease Sickle Cell Anemia|Sickle Cell Disorders|Hemoglobin Beta Thalassemia Disease |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Immune Mediated Anemia|Immune Mediated Thrombocytopenia|Chronic GVHD |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06071520 | Completed | Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Fundación Pública Andaluza para la gestión de la Investigación en Sevilla |
March 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05613296 | Not yet recruiting | ITP - Immune Thrombocytopenia|Chronic ITP|Refractory ITP |
Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell''Adulto |
February 2023 | -- |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Myelofibrosis|Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine|Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 3 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04904276 | Terminated | ITP|Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 18 2021 | -- |
Technische ondersteuning
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Als u nog andere vragen heeft, laat dan een bericht achter.
Veelgestelde vragen
Vraag 1:
What’s the difference between S2625 and S2206?
Antwoord:
The differences between S2625 and S2206: 1. S2206 is more stable than S2625; 2. The water solubility of S2206 is better than S2625; 3. The absorption of S2206 is harder than S2625, so you need to test the suitable dosage if you use it in animal assays; 4. The potency of S2206 and S2625 is similar.
