alleen voor onderzoeksdoeleinden
Tivantinib c-Met remmer
Cat.nr.S2753
Chemische structuur
Molecuulgewicht: 369.42
Kwaliteitscontrole
| Gerelateerde doelwitten | EGFR VEGFR PDGFR FGFR Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 c-Kit |
|---|---|
| Overig c-Met Inhibitoren | Tepotinib Dihexa SGX-523 PHA-665752 Foretinib SU11274 BMS-777607 JNJ-38877605 PF-04217903 Savolitinib (AZD6094) |
Celkweek, behandeling & werkzame concentratie
| Cellijnen | Assaytype | Concentratie | Incubatietijd | Formulering | Activiteitsbeschrijving | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNK-45 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| HT29 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| NCI-H441 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | |||
| NCI-H661 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | |||
| NCI-H446 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=7 μM | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.55 μM | |||
| DLD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.53 μM | |||
| A549 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.59 μM | |||
| SK-OV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.66 μM | |||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.6 μM | |||
| A375 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.42 μM | |||
| NCI-H441 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.3 μM | |||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.49 μM | |||
| MKN-45 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.58 μM | |||
| HT29 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | |||
| MKN-45 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | modestly induces apoptosis by 35%. | |||
| MDA-MB-231/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=1.2 μM | |||
| 1833/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=3.7 μM | |||
| EBC1 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | |||
| SNU638 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | |||
| A549 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| H460 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| HCC827 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | |||
| EBC1 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | |||
| H460 | Function assay | 10 μM | inhibits tubulin polymerization | |||
| K562/VCR | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | |||
| CEM/VBL | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | |||
| U266 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.1 μM | |||
| OPM-2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.8 μM | |||
| MM.1S | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.6 μM | |||
| MM.1R | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 49% | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=0.9 μM | |||
| ANBL-6 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| ANLB-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/1 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/R10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| 8226/S | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | |||
| 8226/LR-5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | |||
| Huh7 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=9.9 nM | ||
| Hep3B | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=139.77 nM | ||
| Chang | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Hep3B | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| HepG2 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Chang | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| MHCC97L | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=315 nM | ||
| MHCC97H | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=368 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=265 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=392 nM | ||
| MHCC97L | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| MHCC97L | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| Huh7 | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts | Kinase assay | 25 μM | DMSO | reduces Histone H3 and H4 acetylation levels | ||
| H23 | Growth inhibitory assay | 25 μM | DMSO | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| WM35 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| NIH 3T3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H838 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H1395 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| Quiescent S2 | Kinase assay | 30 μM | DMSO | completely abrogates TSA-induced hyperacetylation of H3K4me3 histones | ||
| PC3 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| Du145 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LAPC-4 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Function assay | 20 μM | DMSO | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| LAPC-4 | Function assay | 20 μM | DMSO | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| SKNO-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| SKNO-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | enhances mitotic catastrophe | ||
| NRK-52E | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits Ang II-induced STAT3 nuclear translocation and the expression of TGF-β1, collagen IV and fibronectin | ||
| PC12 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~12.5 μM | DMSO | prevents TSA-induced neurite formation | ||
| HPMCs | Function assay | reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human peritoneal mesothelial cells | ||||
| A549 | Function assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | affects the viral life cycle and host response | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | ~30 μM | DMSO | reduces pro-inflammatory gene expression | ||
| MEMM | Kinase assay | 15 µM | DMSO | decreases acetylation of histone H3 | ||
| MEMM | Growth inhibitory assay | ~20 µM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| MEMM | Apoptosis assay | 15 µM | DMSO | induces the presence of the apoptosis protein, cleaved Caspase-3 | ||
| T47D | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=72 nM | ||
| ZR-75-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=79 nM | ||
| BT474 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=86 nM | ||
| HCC1954 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=119 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-453 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=975 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3208 nM | ||
| SkBr3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HCT116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=5836 nM | ||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HFF | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=7615 nM | ||
| HN5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=4009 nM | ||
| H157 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2642 nM | ||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>2,500 nM | ||
| SKOV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2126 nM | ||
| OVCAR-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2918 nM | ||
| BXPC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3141 nM | ||
| MiaPaCa | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=5433 nM | ||
| PANC-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=8681 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=147 nM | ||
| DU145 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3812 nM | ||
| PC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| BT474 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 160 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 150 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 43 nM | ||
| PC3 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 49 nM | ||
| KARPAS-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=41 nM | ||
| CCRFSB | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=155 nM | ||
| SUP B15 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=197 nM | ||
| SD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=320 nM | ||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=654 nM | ||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=3602 nM | ||
| Tanoue | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=4517 nM | ||
| RCH-ACV | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=152 nM | ||
| SEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=202 nM | ||
| KASUMI-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=225 nM | ||
| REH | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=288 nM | ||
| 697 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=338 nM | ||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=421 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=812 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=2114 nM | ||
| J.GAMMA-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=65 nM | ||
| JR45.01 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=68 nM | ||
| A3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=69 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=73 nM | ||
| MOLT-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=74 nM | ||
| P116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=78 nM | ||
| J.Cam1.6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=79 nM | ||
| I 9.2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=80 nM | ||
| LOUCY | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=117 nM | ||
| J.RT3-T3.5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=123 nM | ||
| 800000 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=163 nM | ||
| Jurkat | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=225 nM | ||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=232 nM | ||
| Molt-16 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=241 nM | ||
| CEM/C3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=257 nM | ||
| CEM/C2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=271 nM | ||
| CCRFCEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=327 nM | ||
| CEM/C1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=382 nM | ||
| SUPTI[VB] | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=619 nM | ||
| CCRF–HSB-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=2117 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| I 9.2 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| A3 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| RD | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| Rh41 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=33.8 nM | |||
| Rh18 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=303 nM | |||
| Rh30 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=4.81 μM | |||
| BT-12 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-266 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.22 μM | |||
| TC-71 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.52 μM | |||
| CHLA-9 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=591 nM | |||
| CHLA-10 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=102 nM | |||
| CHLA-258 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.05 μM | |||
| GBM2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=9.15 μM | |||
| NB-1643 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=5.4 μM | |||
| NB-Ebc1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-90 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-136 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=265 nM | |||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=6.49 nM | |||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=147 nM | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=40 nM | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=268 nM | |||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=107 nM | |||
| Karpas-299 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.93 μM | |||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=7.35 μM | |||
| H1299 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits IKBKE-induced Akt Activation | |||
| Klik om meer experimentele gegevens over cellijnen te bekijken | ||||||
Chemische informatie, opslag en stabiliteit
| Molecuulgewicht | 369.42 | Formule | C23H19N3O2 |
Opslag (vanaf de datum van ontvangst) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-nr. | 905854-02-6 | SDF downloaden | Opslag van stamoplossingen |
|
|
| Synoniemen | ARQ 197 | Smiles | C1CC2=C3C(=CC=C2)C(=CN3C1)C4C(C(=O)NC4=O)C5=CNC6=CC=CC=C65 | ||
Oplosbaarheid
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 73 mg/mL
(197.6 mM)
Ethanol : 35 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molariteitscalculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo formulatiecalculator (heldere oplossing)
Stap 1: Voer onderstaande informatie in (Aanbevolen: een extra dier om rekening te houden met verlies tijdens het experiment)
Stap 2: Voer de in vivo formulering in (Dit is alleen de calculator, geen formulering. Neem eerst contact met ons op als er geen in vivo formulering is in de sectie oplosbaarheid.)
Berekeningsresultaten:
Werkconcentratie: mg/ml;
Methode voor het bereiden van DMSO-moedervloeistof: mg geneesmiddel vooropgelost in μL DMSO ( Concentratie moedervloeistof mg/mL, Neem eerst contact met ons op als de concentratie de DMSO-oplosbaarheid van de batch van het geneesmiddel overschrijdt. )
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO moedervloeistof, voeg daarna toeμL PEG300, mengen en verhelderen, daarna toevoegenμL Tween 80, mengen en verhelderen, daarna toevoegen μL ddH2O, mengen en verhelderen.
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO moedervloeistof, voeg daarna toe μL Maïsolie, mengen en verhelderen.
Opmerking: 1. Zorg ervoor dat de vloeistof helder is voordat u het volgende oplosmiddel toevoegt.
2. Zorg ervoor dat u het/de oplosmiddel(en) in de juiste volgorde toevoegt. U moet ervoor zorgen dat de verkregen oplossing, bij de vorige toevoeging, een heldere oplossing is voordat u verdergaat met het toevoegen van het volgende oplosmiddel. Fysieke methoden zoals vortexen, ultrasoon of een warmwaterbad kunnen worden gebruikt om het oplossen te bevorderen.
Werkingsmechanisme
| Kenmerken |
The first selective c-Met inhibitor to be advanced into human clinical trials.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
c-Met
(Cell-free assay) 0.355 μM(Ki)
|
| In vitro |
Van ARQ-197 is aangetoond dat het HGF/c-Met-geïnduceerde cellulaire reacties in vitro voorkomt. Deze verbinding bezit antitumorale activiteit; het remt de proliferatie van A549-, DBTRG- en NCI-H441-cellen met een IC50 van 0,38, 0,45, 0,29 μM. Behandeling met dit middel resulteert in een afname van de fosforylering van de MAPK-signaalcascade en preventie van invasie en migratie. Bovendien zorgt ectopische expressie van c-Met in NCI-H661, een cellijn zonder endogene expressie van c-Met, ervoor dat het een invasief fenotype verwerft dat ook wordt onderdrukt door dit chemische middel. Hoewel de toevoeging van toenemende concentraties van deze remmer de Km van ATP niet significant beïnvloedt, verminderde blootstelling van c-Met aan 0,5 μM van deze substantie de Vmax van c-Met met ongeveer 3-voudig. Het vermogen van dit molecuul om de Vmax te verlagen zonder de Km van ATP te beïnvloeden, bevestigde dat het c-Met remt via een niet-ATP-competitief mechanisme en kan daarom de hoge mate van kinase-selectiviteit verklaren. Het verhindert humaan recombinant c-Met met een berekende remmingsconstante Ki van ongeveer 355 nM. Hoewel de hoogst gebruikte ATP-concentratie 200 μM is, wordt de potentie van dit compound tegen c-Met niet verminderd door ATP-concentraties tot 1 mM te gebruiken. Het blokkeert c-Met-fosforylering en stroomafwaartse c-Met-signaalroutes. Dit chemische middel onderdrukt constitutieve en ligand-gemedieerde c-Met-autofosforylering en, bij uitbreiding, c-Met-activiteit, wat op zijn beurt leidt tot de remming van stroomafwaartse c-Met-effectoren. De inductie van caspase-afhankelijke apoptose wordt verhoogd in c-Met-expresserende menselijke kankercellen, waaronder HT29-, MKN-45- en MDA-MB-231-cellen. |
| Kinase Assay |
c-Met SDS-PAGE in vitro kinase-assay
|
|
Recombinant c-Met-eiwit (100 ng) wordt gedurende 30 minuten bij kamertemperatuur voor-geïncubeerd met toenemende concentraties van deze verbinding. Na pre-incubatie worden 100 μM poly-Glu-Tyr-substraat en verschillende concentraties ATP met 5 μCi [γ-32P]ATP aan het reactiemengsel toegevoegd. De reactie wordt 5 minuten bij kamertemperatuur geïncubeerd en vervolgens gestopt door de toevoeging van 5 μL SDS-polyacrylamidegel, reducerende monsterbuffer. De monsters worden vervolgens op een 7,5% acrylamidegel geladen en SDS-PAGE wordt uitgevoerd. De gefosforyleerde poly-Glu-Tyr-substraten worden uiteindelijk gevisualiseerd door autoradiografie. De c-Met-activiteit wordt gekwantificeerd door densitometrie.
|
|
| In vivo |
Alle drie de met Tivantinib behandelde xenograftmodellen vertonen een vermindering van de tumorgroei: 66% in het HT29-model, 45% in het MKN-45-model en 79% in het MDA-MB-231-model. In deze xenograftstudies werden geen significante veranderingen in het lichaamsgewicht waargenomen na orale toediening van deze verbinding bij 200 mg/kg. Farmacodynamisch wordt de fosforylering van c-Met in humane colon-xenografttumoren (HT29) sterk geremd door dit chemische middel, zoals beoordeeld door een dramatische vermindering van c-Met-autofosforylering 24 uur na een enkele orale dosis van 200 mg/kg van dit middel. Dezelfde dosering bij muizen toont aan dat tumorxenografts worden blootgesteld aan aanhoudende plasmaconcentraties van de verbinding, consistent met de waargenomen farmacodynamische remming van c-Met-fosforylering en remming van de proliferatie van c-Met-bevattende kankercellijnen. Plasmaconcentraties van het middel 10 uur na dosering bleken 1,3 μM te zijn, meer dan 3 keer boven de biochemische remmingsconstante van deze stof voor c-Met. Daarom is het in staat om zijn doelwit in vivo in het xenografted menselijke tumorweefsel te onderdrukken. Concluderend blokkeert deze remmer de groei van c-Met-afhankelijke xenografted menselijke tumoren. |
Referenties |
|
Toepassingen
| Methoden | Biomarkers | Afbeeldingen | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | cMET / p-cMET / p-AKT / p-ERK / p-rpS6 |
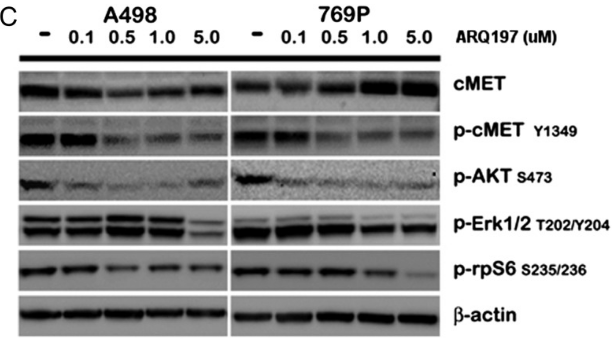
|
23022995 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
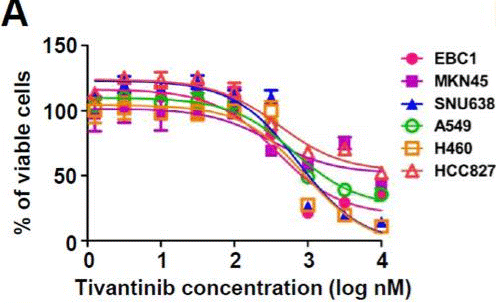
|
23598276 |
Informatie over klinische proeven
(gegevens van https://clinicaltrials.gov, bijgewerkt op 2024-05-22)
| NCT-nummer | Werving | Aandoeningen | Sponsor/medewerkers | Startdatum | Fasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02150733 | Completed | Hepatic Impairment|Solid Tumor|Cancer |
Daiichi Sankyo|Medpace Inc. |
April 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01892527 | Completed | Colorectal Cancer Metastatic|C-met Overexpression |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
March 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02049060 | Completed | Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma|Nonsquamous Nonsmall Cell Neoplasm of Lung |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
January 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT01755767 | Completed | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
Daiichi Sankyo|ArQule Inc. a subsidiary of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC a subsidiary of Merck & Co. Inc. (Rahway NJ USA) |
December 27 2012 | Phase 3 |
Technische ondersteuning
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Als u nog andere vragen heeft, laat dan een bericht achter.
Veelgestelde vragen
Vraag 1:
Are there any other solutions (apart from DMSO) I can dissolve it for in vivo experiment?
Antwoord:
S2753 This compound (ARQ 197) can be dissolved in 1% methylcellulose at 15 mg/ml as a suspension.
